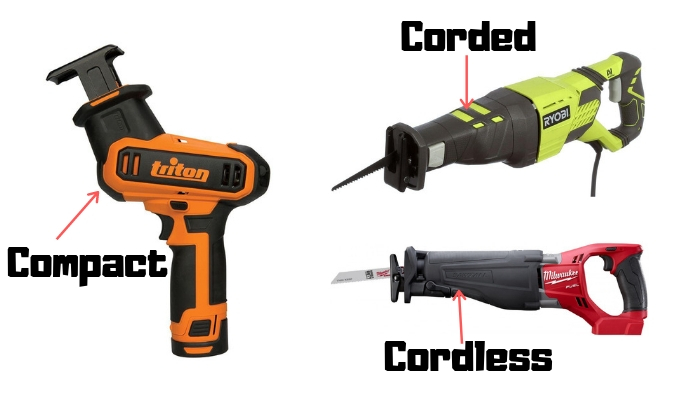
When it comes to fast cutting and demolition tasks, you have several different types of reciprocating saws you can choose from to do the job. You may find the power of a corded reciprocating saw essential for your project, or you may value the portability of a cordless model more.
For tight spaces, few tools can beat the versatility of a compact or one handed reciprocating saw. And if you happen to have a suitable air compressor, then the reliability and power of a pneumatic reciprocating saw may be just what you’re looking for.
Corded Reciprocating Saws
Like most power tools you probably have already in your home or workshop, the corded reciprocating saw draws its power from a wall outlet or extension cord.
This constant source of power also means that you get virtually unlimited running time out of your tool, and you don’t need to worry about changing batteries or your reciprocating saw fading out in the middle of a cut.
Corded Reciprocating Saw Advantages and Disadvantages
Corded reciprocating saws are widely available on the market, and if you’re shopping for a tool within a budget, having a wide selection is always a great thing. Aside from their availability, corded reciprocating saws are also relatively inexpensive compared to the other types, as well.
The main advantage of a corded reciprocating saw, however, is their reliable power. You can keep on cutting and not have to worry about your battery or fuel level, and you get consistent power every time. Plus, corded models usually come with more powerful motors since the manufacturer can focus more on output without having to worry about energy efficiency as much.
On the other hand, a corded saw is limited by the reach of its cord – which can be an issue if you’re working onsite, or outdoors. There’s also the possibility of the tool accidentally sawing through the power cord, as well as the other hazards that a cord can present in the workplace.
Corded Reciprocating Saw Power Rating
Corded reciprocating saws come with AC, DC or universal electric motors, and these are rated in terms of amperes, or amps. The higher the amp rating, the more powerful the tool is, and the tougher the work it can do. Corded saw models start at around 7 amps for home use, and go all the way to 15 amps or more.
For light duty tasks such as pruning small branches and occasionally cutting through drywall, around 7 to 10 amps will give you good results. For working on wood, hardwood, and metal, you will need/wish you had a reciprocating saw rated at 11 amps or higher.
Corded reciprocating saws also have a voltage rating. It’s important to make note of this since plugging in a power tool into an outlet with a mismatched voltage will likely damage it. The voltage of your corded reciprocating saw, however, has no bearing on its performance.
Cordless Reciprocating Saws
Cordless reciprocating saws run off their own battery packs. This makes them the most convenient choice to carry with you, as you are not constricted by a power cord.
This portability also makes them the reciprocating saw of choice for most outdoor work, as well as for jobs that you need to do on top of ladders or scaffolding.
Cordless Reciprocating Saw Advantages and Disadvantages
Cordless reciprocating saws are very convenient to have, and they let you work just about anywhere. Newer models with Lithium-ion batteries and brushless motors now also offer performance comparable to corded models, as well. For outdoor work, a cordless reciprocating saw is easily the more practical choice.
The limited running time of a battery operated tool, however, is always the main disadvantage of a cordless reciprocating saw. Aside from the downtime of having to charge your batteries, cordless models are expensive as well – especially the brushless models. Plus, the added weight of the battery pack makes a cordless saw significantly heavier, too.
Cordless Reciprocating Saw Power Rating
Cordless reciprocating saws also come with electric motors, but their power are compared in terms of voltage instead. The higher the voltage, the more powerful your cordless reciprocating saw is, generally speaking. The battery plays a part in this equation as well, but for the most part, cordless saws can start at 12 volts, on to 15, 18, 24 and 36 volts.
For light tasks around the house or outside, a cordless reciprocating saw with a 12-volt motor and battery combo will serve you well. Demolition tasks, on the other hand, are best done with an 18-volt cordless model, at least.
Battery life is also a big deal when it comes to comparing cordless reciprocating saws. For power tools, battery capacity is often given in terms of amp-hours, and the higher the battery Ah rating, the bigger is its capacity.
Compact / One Handed Reciprocating Saws
Compact reciprocating saws are designed so that you can operate them with one hand, and their size makes them convenient for working in tight spaces, or if you simply prefer having a lighter tool.
They are ideal for getting in between studs, or for doing a lot of overhead cuts. Compact reciprocating saws can either be corded or cordless and there also compact air powered models as well.
Compact Reciprocating Saw Advantages and Disadvantages
Compact reciprocating saws are the tool of choice for working in tight spaces, especially ones that you can’t fit two hands into. For working in wall interiors, plumbing closets and crawl spaces, a compact saw is simply much easier to handle compared to a full-size reciprocating saw, and even more so if you get a cordless model.
On the other hand, compact reciprocating saws can only do so much with the smaller motors they come with. This makes them less than ideal for demolition tasks, or for cutting through large amounts of material. Most compact reciprocating saws can only take the smaller saw blades, as well, which tends to limit your options. Due to their size, you may also have a harder time using a compact saw with both hands, as well.
Compact Reciprocating Saw Power Rating
Compact reciprocating saws can either be cordless or corded. Expect a one-handed reciprocating saw to have smaller amperage or voltage ratings though. For corded compact reciprocating saws, most models will have a 5 Amp motor in a mini form factor. Cordless compact reciprocating saws typically go in the 12 volt to 18-volt range.
There are also mini air saw models available on the market, and they usually start at around 4 cubic feet per minute and rated for 90 PSI or up. For more details on how these ratings compare to regular-sized air saws, refer to the Pneumatic Reciprocating Saw Power Rating section.
Pneumatic Reciprocating Saws
Pneumatic reciprocating saws are also sometimes called air saws, and you will need a suitable air compressor to power one of these tools.
Pneumatic reciprocating saws are usually the preferred tool of choice for industrial applications, and you will often see them in use in chemical plants, gas utilities, refineries, and other work sites where an electrical power tool may be impractical to use.
Pneumatic Reciprocating Saw Advantages and Disadvantages
Pneumatic reciprocating saws do not have an internal motor, and they have a much simpler internal construction compared to the other types of power saws. This makes them extra durable and reliable, which are highly desirable in industrial environments. Since they are powered by compressed air, pneumatic reciprocating saws are also self-cooling, as well. They also run quieter, and they are much lighter compared to corded and cordless electrical models.
Since they need a suitable air compressor to operate, these types of tools are mostly confined to workshops and other areas where a compressed air system is available. It’s not a tool you can use anywhere, unless you bring along a portable air compressor with you as well. Only a limited number of manufacturers build air saws, so your selection can be very limited, too.
Pneumatic Reciprocating Saw Power Rating
Pneumatic reciprocating saws, or air saws, are powered by an air compressor. When it comes to power rating, the important figure to consider here is the air consumption, which is usually given in terms of cubic feet per minute, or CFM. The higher the CFM, the larger the volume of air that the tool can use and the more powerful its air motor is.
Pneumatic reciprocating saws are made for a wide variety of specialized applications, and their CFM ratings can range from as low as 4 CFM to as high as 46 CFM for the handheld models. Mini air saws start at around 4 CFM, and these are already powerful enough to be used in metal work. Heavy-duty models start at around 15 CFM, while saws rated 30 CFM and up are used for industrial applications.
Aside from CFM, the larger pneumatic reciprocating saws are also rated in terms of horsepower, or hp, as well. Manufacturers will also prescribe a pressure level needed to operate the tool, given in terms of pounds per square inch or PSI. Most models will work off of 90 to 120 PSI, and these have no bearing on their relative performance.